Friday 25 January, 2013, 13:45 - Radio Randomness, Spectrum Management
Wireless Waffle received an e-mail from Des of Ireland. Des writes:Since early May I have been noticing many many frequencies being occupied by very short bursts of digital 'noise' which are random in their frequency and time but very recognisable. So far pattern emerged is that they follow an 8 kHz spacing right across the HF bands (from 3.4 MHz to 28.5 MHz), but mainly in 6 to 9 MHz region. Even 6622kHz Shanwick being clobbered ... These noise bursts in the HF bands intrigue me, I wondered if it is a basic military comms set-up in case satellites/internet/microwave/fible-cable are clobbered.
Take a look a the picture below (click on it to open a much larger version). It is a snapshot of the radio spectrum between roughly 6550 and 6950 kHz taken using the University of Twente's on-line receiver in the Netherlands (which is a marvel in itself). The snapshot was taken at about 07:00 GMT. The horizontal axis shows the frequency, the vertical axis is time (in thie case about a minute). Straight vertical lines represent constant transmissions. Dotted ones (such as the broken line just above 6600 kHz) are morse code. Other squiggles that are roughly vertical are all manner of other signals that can be found on the HF bands.
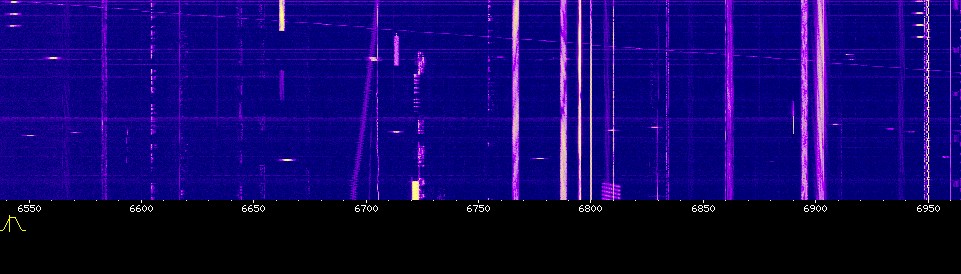
What is of interest here are the horizontal dashes of which there are three at the top left hand corner (just under 6550 kHz), four just below 6950 kHz and various others scattered across the chart, seemingly randomly (see around 6665 kHz and 6555 kHz for two bright ones). These are not bugs in the University's software, nor are they local interference in Twente. What they are are bursts of data from a frequency hopping transmitter. If you tune into one of the frequencies just at the time when the transmission is taking place on that frequency, you will hear a 'chuff' noise which is the quick burst of data that is being sent. If you happen across a frequency that has multiple 'hops' on it, the effect is not totally unlike there being a steam train on the frequency (listen to this actual recording).
At HF, this hopping transmission is almost certainly military in nature. Frequency hopping at HF is not at all uncommon. Even back in the 1980s, Racal's TRA 931XH would happily hop around the HF bands. In the case of the '931XH it did this by changing frequency roughly every second. Transmissions were just SSB (with an initial data burst to synchronise the receiver and transmitter - this is essential so that the two follow the same sequence of frequencies). The Wireless Waffle team had the fun of seeing a demo of the '931XH which was set to hop from frequencies between around 6950 and 7450 kHz, right across the 41m broadcast band. The effect of the hopping was to change the background noise every second or so - sometimes with a loud whistle caused by the carriers of the broadcast signals. The effect to anyone who happened to listen on a frequency that was being used would have been that they would have heard speech for a second which would then disappear.
 There's nothing unusual about the use of frequency hopping transmitters. Your bluetooth headset does this, and most GSM networks are set up to use frequency hopping too. The reason for using frequency hopping can be many and various, such as:
There's nothing unusual about the use of frequency hopping transmitters. Your bluetooth headset does this, and most GSM networks are set up to use frequency hopping too. The reason for using frequency hopping can be many and various, such as:- Hopping around makes the transmission much more difficult to detect. Unless you know the sequence of frequencies being used, it's almost impossible to follow the transmission from one frequency to the next.
- Hopping can overcome some kinds of interference. If one frequency is blocked (from a broadcast transmission for example) the information sent on that frequency is lost, but if most are clear of interference, the error correction schemes can be arranged to deal with missing blocks and the overall communication is unaffected.
- Hopping can help overcome fading and propagation problems. In a GSM network for example, Rayleigh fading will cause some channels to have deep fades and others not. Hopping around makes sure that these 'dead' channels do not cause a total lack of communication.
Lee carberry
Sunday 10 February, 2013, 16:01
I have been hearing that noise right across HF for YEARS now and always assumed it was military in nature. After many hours of listening following that ' chuff ' noise I have sometimes been rewarded with a short burst of voice comms' , usually just a brief pronouncement of numbers and letters ,obviuosly some sort of coded message. Thanks for a very interesting article WW !